在编译Openharmony的时候,经常出现类似如下错误:exceptions.ohos_exception.OHOSException: subsystem name config incorrect in '/root/tf/new_openharmony/vendor/hihope/dayu210/ohos.build', build file subsystem name is product_hihope,configured subsystem name is product_dayu210。这是因为白名单设置问题导致,所以需要修改白名单,如下是思路
一、相关文件
对于白名单文件,涉及到的是compile_standard_whitelist.json,此文件在build仓库目录下。
二、"bundle_subsystem_error"
"bundle_subsystem_error"是用于检测是否存在子系统,在hb/services/loader.py中将其获取到bundle_subsystem_allow_list中
bundle_subsystem_allow_list = compile_standard_allow_info.get("bundle_subsystem_error", [])
在hb/util/loader/load_ohos_build.py中会根据build_files来遍历subsystem名字,如果不匹配则报错。逻辑如下
if _subsystem_name != self._subsystem_name: is_allow = False for file_path in self._bundle_subsystem_allow_list: if _build_file.endswith(file_path): is_allow = True break if is_allow: print("warning: subsystem name config incorrect in '{}', build file subsystem name is {}," "configured subsystem name is {}.".format( _build_file, _subsystem_name, self._subsystem_name)) else: raise OHOSException("subsystem name config incorrect in '{}', build file subsystem name is {}," "configured subsystem name is {}.".format( _build_file, _subsystem_name, self._subsystem_name), 2014)
针对此,我们需要将我们的3588仓库添加到compile_standard_whitelist.json中,如下
+ "device/board/hihope/dayu210/ohos.build", + "vendor/hihope/dayu210/ohos.build"
三、"subsystem_components"
这里涉及子系统和组件的白名单,如果需要编译相关的组件,则需要添加,我这里添加如下:
@@ -32,6 +45,15 @@ "//device/soc/rockchip/rk3568/hardware/omx_il/component/video/enc:libomxvpu_enc", "//device/soc/rockchip/rk3568/hardware/omx_il/core:libOMX_Core", "//device/soc/rockchip/rk3568/hardware/omx_il/libOMXPlugin:libOMX_Pluginhw", + "//device/soc/rockchip/rk3568/hardware/npu:libnpu_vdi_impl", + "//device/soc/rockchip/rk3588/hardware/codec:libcodec_oem_interface", + "//device/soc/rockchip/rk3588/hardware/display:display_composer_vendor", + "//device/soc/rockchip/rk3588/hardware/display:display_gfx", + "//device/soc/rockchip/rk3588/hardware/display:libdisplay_buffer_vdi_impl", + "//device/soc/rockchip/rk3588/hardware/display:libdisplay_buffer_vendor", + "//device/soc/rockchip/rk3588/hardware/display:libdisplay_composer_vdi_impl", + "//device/soc/rockchip/rk3588/hardware/display:libhigbm_vendor", + "//device/soc/rockchip/rk3588/hardware/mpp/mpp-develop/mpp/legacy:rockchip_vpu",
在out/rk3588/build_configs/parts_info/part_subsystem.json中的内容会在编译的时候解析,如果不匹配则按照如下逻辑出错
for component in components_name: if component['component'] in list(subsystem_compoents_whitelist_info.keys()): continue overrided_components_name = '{}_{}'.format(component['component'], 'override') if component['component'] in list(part_subsystem_component_info.keys()) \ or overrided_components_name in list(part_subsystem_component_info.keys()): if subsystem_name in list(part_subsystem_component_info.values()): continue if subsystem_name == component['component']: continue name = subsystem_name message = "find subsystem {} failed, please check it in {}.".format(subsystem_name, config_path) else: name = component['component'] message = "find component {} failed, please check it in {}.".format(component['component'], config_path) if name in subsystem_components_list: print(f"Warning: {message}") else: raise Exception(message)
这里涉及两方面,一个是vendor/hihope/dayu210/config.json,这是Openharmony产品需要打开的功能配置,会生成part_subsystem.json
另一个是仓库本身的bundle.json,这里会声明此仓库属于哪个subsystem和哪个component,所以如果不匹配就会出现
3.1 "gn_part_or_subsystem_error"
"gn_part_or_subsystem_error"用来判断build_configs/parts_info/part_subsystem.json的subsystems name和gn的BUILD.gn的subsystem是否对应,如果不对应,则按照下面逻辑报错
if subsystems_name is None or subsystems_name == '' or subsystems_name != args.subsystem_name: message = f"subsystem name or part name is incorrect, " \ f"target is {args.target_path}, subsystem name is {args.subsystem_name}, " \ f"part name is {args.part_name}" if args.target_path in bundle_file_allow_list: print(f"[0/0] warning: {message}") else: raise Exception(message)
3.2 "deps_added_external_part_module"
"deps_added_external_part_module"是依赖模块的白名单检测,对应BUILD.gn的deps,如果依赖存在异常,则如下逻辑报错
for dep in args.deps: dep_path = get_path_from_label(dep) if dep_path.find('third_party/rust/crates') != -1: continue if dep_path.find('third_party') != -1: dep_part = get_dep_part(dep_path, third_party_info) tips_info = "{} depend part {}, need set part deps {} info to".format( args.target_path, dep, dep_part) check_third_party_deps(args, dep_part, parts_deps_info, tips_info, third_deps_allow_list) continue match_flag = False for pattern in part_pattern: if dep_path.startswith(pattern): match_flag = True break if match_flag is False: message = "deps validation part_name: '{}', target: '{}', dep: '{}' failed!!!".format( args.part_name, args.target_path, dep) if args.target_path in deps_allow_list: print(f"[0/0] WARNING:{message}") else: raise Exception(message)
3.3 "external_deps_added_self_part_module"
"external_deps_added_self_part_module"是外部依赖的白名单检测,对应BUILD.gn的external_deps,如果依赖存在异常,则如下逻辑报错
if external_part_name == args.part_name: message = "{} in target {} is dependency within part {}, Need to used deps".format( external_part_name, args.target_path, args.part_name) if args.target_path in added_self_part_allow_list: print(f"[0/0] WARNING: {message}") return else: raise Exception(message)
3.4 "external_deps_bundle_not_add"
"external_deps_bundle_not_add"同上一致,但是他会按照如下逻辑报错
part_deps_info = parts_deps_info.get(args.part_name) if not part_deps_info: _warning_info = "{} {}.".format(_tips_info, args.part_name) elif not part_deps_info.get('components') or \ not external_part_name in part_deps_info.get('components'): _warning_info = "{} {}.".format(_tips_info, part_deps_info.get('build_config_file')) else: _warning_info = "" if _warning_info != "": if args.target_path in bundle_not_add_allow_list: print(f"[0/0] WARNING: {_warning_info}") else: raise Exception(_warning_info)
3.5 "third_deps_bundle_not_add"
"third_deps_bundle_not_add"是第三方依赖白名单,如果白名单没有第三方依赖库,则按照如下逻辑报错
def check_third_party_deps(args, dep_part, parts_deps_info, _tips_info, third_deps_allow_list): """check whether the three-party dependency is in the part declaration""" if args.part_name == dep_part: return part_deps_info = parts_deps_info.get(args.part_name) if not part_deps_info: _warning_info = f"{_tips_info} {args.part_name}." elif not part_deps_info.get('third_party') or \ not dep_part in part_deps_info.get('third_party'): _warning_info = f"{_tips_info} {part_deps_info.get('build_config_file')}." else: _warning_info = "" if _warning_info != "": if args.target_path in third_deps_allow_list: print(f"[0/0] WARNING: {_warning_info}") else: raise Exception(_warning_info) return
四、总结
至此,我们可以知道,如果我们需要添加新的平台,我们需要将其仓库都添加到白名单中。这样Openharmony才能正常编译
五、参考链接
https://forums.openharmony.cn/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=1864&extra=
Openharmony4.0的版本在内核上不支持rk8602的regulator驱动,这就导致两路cpu大核无法正常上电,npu无法正常上电,因为rk860x给cpu和npu提供了真实的regulator。
一、设备树
在rk3588s上,我们可以通过设备树知道cpub0和cpub1以及npu的供电情况如下:
&rknpu { rknpu-supply = <&vdd_npu_s0>; mem-supply = <&vdd_npu_mem_s0>; }; &cpu_b0 { cpu-supply = <&vdd_cpu_big0_s0>; mem-supply = <&vdd_cpu_big0_mem_s0>; }; &cpu_b2 { cpu-supply = <&vdd_cpu_big1_s0>; mem-supply = <&vdd_cpu_big1_mem_s0>; };
对于此,我们可以知道npu和cpu上都需要两路实际的电源供应,对于驱动,则需要如下获取regulator的引用节点
rknpu_supply = devm_regulator_get(&pdev->dev, "rknpu"); cpu_supply = devm_regulator_get(&pdev->dev, "cpu"); mem_supply = devm_regulator_get(&pdev->dev, "mem");
然后再通过上电时机将此路电源打开
ret = regulator_enable(rknpu_supply); ret = regulator_enable(cpu_supply); ret = regulator_enable(mem_supply);
基于此,我们可以知道,对于rk3588s而言,这类regulartor是核心的上电要求,所以我们不能忽略,如下可以找到regulator的设备树定义
vdd_cpu_big0_s0: vdd_cpu_big0_mem_s0: rk8602@42 { compatible = "rockchip,rk8602"; reg = <0x42>; vin-supply = <&vcc5v0_sys>; regulator-compatible = "rk860x-reg"; regulator-name = "vdd_cpu_big0_s0"; regulator-min-microvolt = <550000>; regulator-max-microvolt = <1050000>; regulator-ramp-delay = <2300>; rockchip,suspend-voltage-selector = <1>; regulator-boot-on; regulator-always-on; regulator-state-mem { regulator-off-in-suspend; }; }; vdd_cpu_big1_s0: vdd_cpu_big1_mem_s0: rk8603@43 { compatible = "rockchip,rk8603"; reg = <0x43>; vin-supply = <&vcc5v0_sys>; regulator-compatible = "rk860x-reg"; regulator-name = "vdd_cpu_big1_s0"; regulator-min-microvolt = <550000>; regulator-max-microvolt = <1050000>; regulator-ramp-delay = <2300>; rockchip,suspend-voltage-selector = <1>; regulator-boot-on; regulator-always-on; regulator-state-mem { regulator-off-in-suspend; }; }; vdd_npu_s0: vdd_npu_mem_s0: rk8602@42 { compatible = "rockchip,rk8602"; reg = <0x42>; vin-supply = <&vcc5v0_sys>; regulator-compatible = "rk860x-reg"; regulator-name = "vdd_npu_s0"; regulator-min-microvolt = <550000>; regulator-max-microvolt = <950000>; regulator-ramp-delay = <2300>; rockchip,suspend-voltage-selector = <1>; regulator-boot-on; regulator-always-on; regulator-state-mem { regulator-off-in-suspend; }; };
二、驱动
根据上述可以知道,我们必须要使能这个regulator电,并且此电的设备树节点是rk8602,rk8603.故需要移植驱动
针对此,可以找到驱动文件drivers/regulator/rk860x-regulator.c,其相关的compatible如下
static const struct of_device_id rk860x_dt_ids[] = { { .compatible = "rockchip,rk8600", .data = (void *)RK860X_CHIP_ID_00 }, { .compatible = "rockchip,rk8601", .data = (void *)RK860X_CHIP_ID_01 }, { .compatible = "rockchip,rk8602", .data = (void *)RK860X_CHIP_ID_02 }, { .compatible = "rockchip,rk8603", .data = (void *)RK860X_CHIP_ID_03 }, { } };
这里可以知道,一份驱动对应了多个compatible,可以实现多个节点的不同配置。这样我们可以确定移植此驱动即可。
对于vendor/drivers/regulator/Makefile 添加如下
obj-$(CONFIG_REGULATOR_RK860X) += rk860x-regulator.o
对于vendor/drivers/regulator/Kconfig 添加如下
config REGULATOR_RK860X tristate "Rockchip RK860X Regulator" depends on I2C select REGMAP_I2C help This driver supports Rockchip RK860X Digitally Programmable Buck Regulator. The RK860X is a step-down switching voltage regulator that delivers a digitally programmable output from an input voltage supply of 2.5V to 5.5V. The output voltage is programmed through an I2C interface.
对于arch/arm64/configs/rockchip_linux_defconfig添加如下
CONFIG_REGULATOR_RK860X=y
至此,两路cpu大核和npu的电即可正常输出
我们适配的板子,没办法使用hdc命令,这导致我们调试很不方便,这里提供了修改方法,打开了内核的设备树配置,从而上层能够使用hdc,本文用作记录方法。
一、设备树
我们知道usb需要支持org,那么我们需要将其功能正常打开,这里typec对于usb3,所以如下修改:
diff --git a/rk3588/kernel/arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/rk3588-tianqi-linux.dts b/rk3588/kernel/arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/rk3588-tianqi-linux.dts index cbfdae3..c1c4403 100755 --- a/rk3588/kernel/arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/rk3588-tianqi-linux.dts +++ b/rk3588/kernel/arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/rk3588-tianqi-linux.dts @@ -61,20 +61,22 @@ }; &usbdrd3_0 { - status = "disable"; + status = "okay"; }; &usbdrd_dwc3_0 { dr_mode = "otg"; - status = "disable"; + status = "okay"; + usb-role-switch; }; &usbhost3_0 { - status = "disabled"; + status = "okay"; }; &usbhost_dwc3_0 { - status = "disabled"; + status = "okay"; };
这里可以很清楚的知道需要打开typec对应的usb即可。这里usb-role-switch对照代码看一下就明白了,没什么好讲的。
二、编译
根据板子的配置,我们可以跳到内核目录下,直接编译即可
cd out/kernel/src_tmp/linux-5.10 && ./make-ohos.sh TQ3588
三、烧录
这里直接烧录boot_linux分区即可,如果不想手动做上述操作,可以这个位置(10.3.3.110)拿一下内核
/home/develop/product/embedded/01-openharmony/01-version/2024-11-05-天启板子支持hdc/boot_linux.img
四、使用
这样,hdc能够正常的list
C:\>hdc list targets 9b01005932503033320045da20422900
hdc能够正常进入
C:\>hdc shell # ls / bin data etc lost+found storage tmp chip_prod dev init mnt sys updater chipset eng_chipset lib module_update sys_prod vendor config eng_system lib64 proc system
我们在做openharmony版本的weekly build的时候,需要使用kyPacker来打包update镜像,本文介绍kypacker的使用
一、仓库地址
kypacker仓库地址如下:
https://gitlab2.kylin.com/sh-product-Embedded/openharmony/kypacker
二、使用方法
获取仓库后,我们可以先运行一下make,这样能够获取平台相关的crc32库librkcrc32.so,如果不执行make,则使用python实现的crc32.
2.1、 准备package-file文件
为了能够让kypacker正常工作,需要package-file文件,此文件需要描述文件名字和文件位置,举例如下
package-file package-file bootloader Image/rk3588_spl_loader_v1.11.112.bin parameter Image/parameter.txt uboot Image/uboot.img boot Image/boot.img rootfs Image/rootfs.img userdata Image/userdata.img
2.2、准备需要打包文件
根据package-file,我们需要将文件放在Image目录下的位置,举例如下
-rwxrwx--- 1 root vboxsf 100M 12月 26 09:36 boot.img -rwxrwx--- 1 root vboxsf 369 12月 21 17:15 parameter.txt -rwxrwx--- 1 root vboxsf 457K 12月 26 09:24 rk3588_spl_loader_v1.11.112.bin -rwxrwx--- 1 root vboxsf 100M 12月 26 09:36 rootfs.img -rwxrwx--- 1 root vboxsf 4.0M 12月 22 14:38 uboot.img -rwxrwx--- 1 root vboxsf 100M 12月 26 09:36 userdata.img
2.3、 打包firmware固件
在打包update之前,我们需要打包firmware固件,通过如下命令
kyPacker.py afptool pack ./tests ./tests/Image/firmware.img
至此,可以在./tests/Image/firmware.img查看firmware.img文件
2.4、 打包update
如果firmware.img生成成功,则可以打包update.img,如下命令
kyPacker.py imgmker pack RK3588 ./tests/Image/bootloader.img ./tests/Image/firmware.img -os_type androidos
至此,可以在当前目录上发现update.img文件,打包update.img成功。
三、详情参考
为了更加了解kypacker的工作方式,可以参考仓库的readme.md,如下
https://gitlab2.kylin.com/sh-product-Embedded/openharmony/kypacker
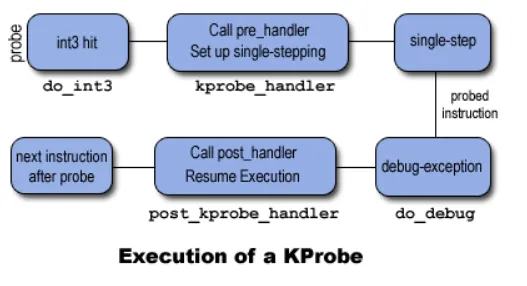
为了调试内核,我们经常会使用kprobe来调试程序,目前的kprobe挂在了ftrace框架下,所以我们有必要讲一下kprobe/kretprobe,它非常有助于我们调试内核。本文以一个例子来展示kprobe/kretprobe的使用,从而让大家具备调试内核的基本能力
一、什么是KPROBE/KRETPROBE
kprobe是能够动态的进入内核收集函数基本信息的工具,它通过替换指令的方式替换指令的方式,将原本运行在某函数的栈跳到了kprobe的栈,故kprobe能够收集函数的入参,调用栈等基本信息
而kretprobe是改进的kprobe,顾名思义,它可以用于获取函数的返回值信息
所以,kprobe/kretprobe能够获取:
- 寄存器地址
- 内核虚拟地址
- 符号地址
- 堆栈
- 入参
- 返回值 根据此,如下描述是我们了解kprobe必须要记住的:
p[:[GRP/][EVENT]] [MOD:]SYM[+offs]|MEMADDR [FETCHARGS] : Set a probe r[MAXACTIVE][:[GRP/][EVENT]] [MOD:]SYM[+0] [FETCHARGS] : Set a return probe p[:[GRP/][EVENT]] [MOD:]SYM[+0]%return [FETCHARGS] : Set a return probe -:[GRP/][EVENT] : Clear a probe GRP : Group name. If omitted, use "kprobes" for it. EVENT : Event name. If omitted, the event name is generated based on SYM+offs or MEMADDR. MOD : Module name which has given SYM. SYM[+offs] : Symbol+offset where the probe is inserted. SYM%return : Return address of the symbol MEMADDR : Address where the probe is inserted. MAXACTIVE : Maximum number of instances of the specified function that can be probed simultaneously, or 0 for the default value as defined in Documentation/trace/kprobes.rst section 1.3.1. FETCHARGS : Arguments. Each probe can have up to 128 args. %REG : Fetch register REG @ADDR : Fetch memory at ADDR (ADDR should be in kernel) @SYM[+|-offs] : Fetch memory at SYM +|- offs (SYM should be a data symbol) $stackN : Fetch Nth entry of stack (N >= 0) $stack : Fetch stack address. $argN : Fetch the Nth function argument. (N >= 1) (\*1) $retval : Fetch return value.(\*2) $comm : Fetch current task comm. +|-[u]OFFS(FETCHARG) : Fetch memory at FETCHARG +|- OFFS address.(\*3)(\*4) \IMM : Store an immediate value to the argument. NAME=FETCHARG : Set NAME as the argument name of FETCHARG. FETCHARG:TYPE : Set TYPE as the type of FETCHARG. Currently, basic types (u8/u16/u32/u64/s8/s16/s32/s64), hexadecimal types (x8/x16/x32/x64), VFS layer common type(%pd/%pD), "char", "string", "ustring", "symbol", "symstr" and bitfield are supported. (\*1) only for the probe on function entry (offs == 0). Note, this argument access is best effort, because depending on the argument type, it may be passed on the stack. But this only support the arguments via registers. (\*2) only for return probe. Note that this is also best effort. Depending on the return value type, it might be passed via a pair of registers. But this only accesses one register. (\*3) this is useful for fetching a field of data structures. (\*4) "u" means user-space dereference. See :ref:`user_mem_access`.
上面的描述,大家可以看看,具体内容直接试试即可。
1.1 相关文件
为了能够正常操作kprobe,我们关注如下几个文件:
/sys/kernel/debug/tracing/kprobe_events /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/kprobes /sys/kernel/debug/kprobes/list
这三个文件分别为:
- kprobe事件触发器
- kprobe详细事件
- 打开的kprobe列表
二、示例
这里直接以系统调用open为例,方便大家理解
2.1 kprobe监听系统所有的openat事件
我们知道一个open事件对应内核是do_sys_openat2,所以查看声明如下:
static long do_sys_openat2(int dfd, const char __user *filename, struct open_how *how)
基于此,我们直接打印arg2即可,这里是char *,我们可以通过string打印,如下
echo 'p:kylin do_sys_openat2 filename=+0($arg2):string' > /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/kprobe_events
然后打开trace信息如下:
echo 1 > events/kprobes/kylin/enable
此时日志如下:
systemd-journal-311 [003] d... 394.007790: kylin: (do_sys_openat2+0x0/0x2d0) filename="/run/log/journal/150c911f73834975b41af71e80344144/system.journal" systemd-journal-311 [003] d... 394.576585: kylin: (do_sys_openat2+0x0/0x2d0) filename="/run/log/journal/150c911f73834975b41af71e80344144/system.journal" systemd-journal-311 [003] d... 394.576798: kylin: (do_sys_openat2+0x0/0x2d0) filename="/run/log/journal/150c911f73834975b41af71e80344144/system.journal"
如果无需继续trace,关闭方法如下:
echo 0 > /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/kprobes/kylin/enable echo > /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/kprobe_events
2.2 kretprobe监听系统所有的openat事件
我们知道系统所有的openat系统调用到内核都是调用的do_sys_openat2,而在do_sys_openat2中存在getname函数,其函数声明如下:
struct filename *getname(const char __user *);
此函数返回一个struct filename,而这个结构如下:
struct filename { const char *name; /* pointer to actual string */ const __user char *uptr; /* original userland pointer */ int refcnt; struct audit_names *aname; const char iname[]; };
所以我们可以编写kprobe_events如下:
echo 'r:kprobes/kylin getname arg1=+0($retval):string[1]' > kprobe_events
这里值得注意的是 string[1]的编写,可以参考如下:
The string array type is a bit different from other types. For other base types, <base-type>[1] is equal to <base-type> (e.g. +0(%di):x32[1] is same as +0(%di):x32.) But string[1] is not equal to string. The string type itself represents “char array”, but string array type represents “char * array”. So, for example, +0(%di):string[1] is equal to +0(+0(%di)):string. Bitfield is another special type, which takes 3 parameters, bit-width, bit- offset, and container-size (usually 32). The syntax is: b<bit-width>@<bit-offset>/<container-size>
所以我们直接拿到了char* name字段。此时我们打开kprobe即可,如下:
echo 1 > /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/kprobes/kylin/enable
然后我们直接读取ftrace的pipe即可
cat /sys/kernel/tracing/trace_pipe
我截取了一部分输出,以systemd的journal 服务,可以发现如下日志
systemd-journal-308 [001] d... 58935.290005: kylin: (do_sys_openat2+0x18c/0x2d0 <- getname) arg1={"/run/log/journal/150c911f73834975b41af71e80344144/system.journal"} systemd-journal-308 [001] d... 58935.290339: kylin: (do_sys_openat2+0x18c/0x2d0 <- getname) arg1={"/run/log/journal/150c911f73834975b41af71e80344144/system.journal"} systemd-journal-308 [001] d... 58935.290542: kylin: (do_sys_openat2+0x18c/0x2d0 <- getname) arg1={"/run/log/journal/150c911f73834975b41af71e80344144/system.journal"} systemd-journal-308 [001] d... 58935.290740: kylin: (do_sys_openat2+0x18c/0x2d0 <- getname) arg1={"/run/log/journal/150c911f73834975b41af71e80344144/system.journal"}
这里直接打印了openat的name字段是/run/log/journal/150c911f73834975b41af71e80344144/system.journal
三、总结
至此,我从如何使用上解释了kprobe和kretprobe,相信大家具备基于kprobe的调试基本能力了,如果需要了解原文的,可以查看如下:
https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/trace/kprobetrace.html https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/trace/kprobes.html
如果大家还想深入的,可以查看如下文章:
An introduction to KProbes [LWN.net]
https://lwn.net/Articles/132196/
图示如下: